I have plans to utilize the Lego NXT system for several upcoming robotics projects. The success of these projects depends on the capabilities of the kit’s ultrasonic (US) range finder. I created a test rig with the US sensor and NXT brick and conducted several experiments in order to characterize the sensor.
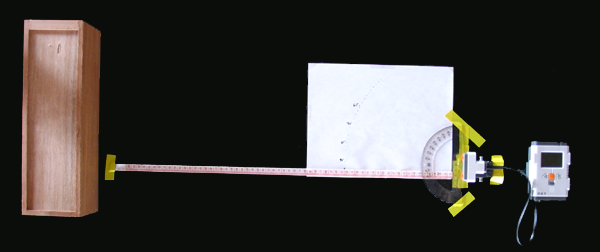
Test rig: wood block, measuring tape, protractor, US sensor, NXT brick (from left to right). Orthogonal Measurements (centimeter increments) Error, Accuracy, and Linearity This experiment used the test rig in which an obstacle was positioned directly in front of the the sensor (orthogonal to the sensor plane). The obstacle was repositioned in centimeter increments from two to 64 centimeters and readings were taken utilizing the built-in “View” ultrasonic reader. A wood block was used as the obstacle to reflect the ultrasonic signal back to the sensor.
The average error over the 63 sample distances is 1.079 cm and the root mean squared error is calculated as 1.662 cm. Figure 1 shows a plot of data points (black points) of perceived distance of the obstacle as a function of the actual distance of the obstacle. The equation of the linear fit (blue line) is y = 0.9757 x + 1.88.
Figure 1. Perceived distance as a function of actual distance.
As is evident from these statistics, a definite linear relationship exists between sensor output and input however an offset error of ~1 cm. This error is likely systematic but future tests will determine if this error is reproducible under varied conditions.
Long Distance Readings Dynamic Range Although the previous test concluded that the sensor operates correctly in the range from 8 to 64 cm, determining the dynamic range of the sensor required determining the upper bound of accurate distance readings. In this experiment, the woodblock was positioned at a distance that caused the NXT block to display “???”. This display indicates that the sensor can not observe any obstacle in front of it. The block was slowly moved closer toward the sensor until a reading was observed on the NXT brick. The sensor finally registered the woodblock at a distance of 207 cm.
As is shown in the first experiment, the sensor accuracy drastically dissintegrates at distances shorter than 8cm. Furthermore the sensor fails entirely at distances greater than 207cm. So, the US sensor has a dynamic range from 8 to 207 cm.
thankyou
we needed this information for a competition we entered